Most of the components of the automobile chassis are connected by bolts. After driving in different road conditions, after being subjected to lateral impact and axial bumps, different degrees of torque attenuation, loose connection, abnormal noise and other failures may occur, which seriously affects driving safety. Through several typical cases of vehicle chassis torque attenuation failure, the failure mechanism is analyzed, and preventive measures are given to provide reference and reference for future design.
introduction
As a kind of mechanical parts commonly used for fastening and connecting, threaded fasteners are convenient, fast and low cost. They are widely used in various industries. They are various in variety, with internal thread structure, external thread structure, full metal self-locking, and structure. Locks, etc.; The function is very different, mainly for connection, fastening, sealing and so on. The paper mainly introduces the mechanism and typical attenuation failure of the automobile chassis bolt fasteners.
1. Fastening mechanism
The bolt fastening connection mainly has the common bolt connection and the bolting connection of the reaming hole. The common bolt connection structure is simple, the disassembly is convenient, and the cost is low. It is the most widely used connection form at present, and most of the installation bolts of the automobile chassis adopt this structure; The bolts can be subjected to large lateral loads by bolting, and the precision of the mounting holes is relatively high. In actual industrial production, the selection of bolts must fully evaluate the working environment and stress of the connected parts, and ensure that it provides a sufficiently reliable fastening connection for the parts to work under extreme conditions. When the bolt is in use, the tightening torque T is applied in advance to pre-tighten, and the bolt axially generates the pre-tightening force F p . The tightening torque T mainly overcomes the frictional resistance torque T 1 generated by the threaded joint surface and the frictional resistance torque T 2 between the annular end surface of the bolt and the contact surface of the workpiece to be joined, namely:
T = T 1 + T 2
During the working process, if the external force produces a torque of M 0 , when M 0 < T, the tightening position and the torque ∑ M = 0, the connection is stable and reliable; when M 0 ≥ T, the tightening position is the combined torque ∑ M ≠0 There is a loosening of the connection position.
2. Typical causes of torque decay of bolt fasteners
Under normal circumstances, the chassis fasteners of the domestic main engine factory will be confirmed by the paint between the fasteners and the connected parts after the vehicle is assembled, so as to confirm the fastening state later. After the vehicle is driven for a period of time, the assembly paint mark is unchanged, the detection torque is within the design requirements, and the connection is reliable; the assembly paint mark is unchanged, and the detection bolt torque is lower than the lower limit of the design requirement, which is the attenuation failure, which is also the focus of the article. The failure mode; the assembly paint mark is misplaced, and the detection torque is lower than the lower limit of the design requirement, which is the looseness failure. In some cases, in order to further ensure the reliability of the fastener connection, the fastener is pre-coated with a thread sealant during assembly. This situation will increase the detection torque after assembly, even exceeding the design limit; In addition, due to the uncertainty caused by the objective factors such as the chemical properties of the thread sealant and the amount of artificial application, the increase of the torque is difficult to summarize and will not be discussed here.
2.1 Low precision of the mounting surface
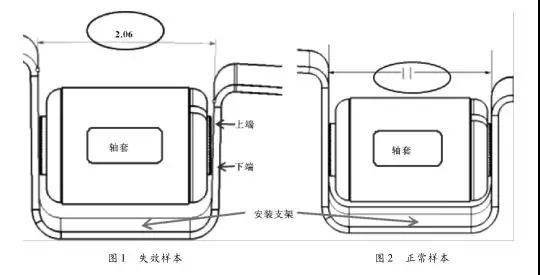
When a model sells back bumps and over-speed belts, the chassis dangling position occasionally emits a “dangdang†noise. During the inspection and inspection of the state of the front suspension components, no obvious interference, bump marks and structural damage were observed, and the paint markings of the fasteners did not cause significant misalignment. The front suspension fastener torque was detected one by one. It was found that the torque of the small bushing mounting bolt of the front suspension lower control arm was attenuated, the detection torque value was 143 N·m, the design standard torque was 210 N·m, and the attenuation amplitude was 32%. After the torque is tightened to the standard torque, the road test is repeated several times, and the abnormal sound is not reproduced. The initial locking failure position is the small arm sleeve mounting position of the control arm. In order to confirm the cause of the problem, disassemble the lower control arm and check that the fastener thread appearance is normal, but the small sleeve mounting sleeve leaves a different depth of indentation on the control arm mounting bracket, and the upper end is shallower than the lower end. This phenomenon indicates that the pressure generated by the contact of the upper and lower end faces of the control arm bushing sleeve with the mounting bracket during the assembly fastening process is different. Use the coordinate measuring instrument to check the mounting bracket plane relationship, there is an angle of 2.06 °, as shown in Figure 1.
Failure analysis. The control arm bushing is bolted to the bracket, and the two mounting faces of the normal sample control arm are in parallel relationship, as shown in Fig. 2; and the failure sample mounting surface has an angle of about 2° as shown in Fig. 1, during the assembly process, Tightening the bolt torque while tightening the axial force, and also losing a part of the torque to correct the upper end angle, so that the mounting surface is in contact with the control arm sleeve. At this time, the mounting bracket is elastically deformed, which is equivalent to the increased screw position. Elastic gasket. As the vehicle is continuously used, the installation position is repeatedly subjected to alternating load, and the mounting bracket gradually changes from elastic deformation to plastic deformation, the installation plane angle becomes smaller, and the elastic deformation support effect is weakened, causing torque attenuation.
Rectification measures:
(1) From the failure analysis, as the vehicle is continuously used, the elastic deformation of the mounting surface will eventually transform into plastic deformation. At this time, the second tightening of the mounting bolt can eliminate the torque attenuation. Since the secondary tightening time is uncertain, the solution is not feasible, but it can be listed in the after-sales maintenance inspection project.
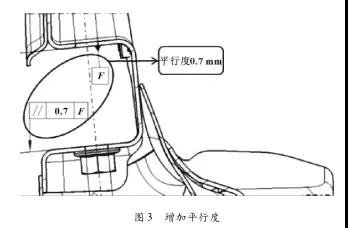
(2) Due to manufacturing tolerances, the mounting surfaces may not be completely parallel, the design increases the parallelism constraint, optimizes the production process, and effectively controls the angular deviation. After verification by the production test, the bushing mounting bracket increases the parallelism by 0.7 mm (as shown in Figure 3), which can effectively control the torque attenuation, meet the design requirements, and the solution is feasible.
  2.2 Improper selection of friction factor
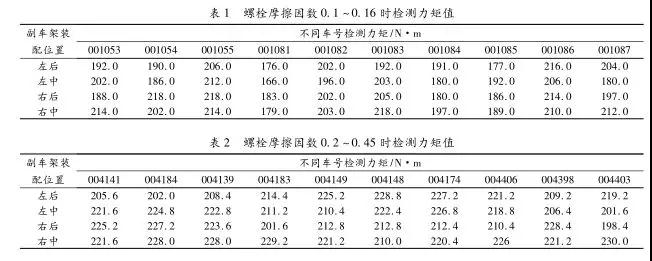
The friction factor is an important parameter of the bolt structure, which directly affects the axial preload force of the bolt and the retention performance of the torque. The initial design state of the front frame and the body mounting bolts of a certain model requires a friction factor of 0.1 to 0. 16, the bolt size is M14 × 1.5, the performance level is 10.9, and the design torque range is (210 ± 20). N·m; After the line is tested by the test field, the assembly paint mark is not moved. The individual torque value is less than the design requirement lower limit of 190 N·m, and the torque has a decay tendency, as shown in Table 1.
Failure analysis. Check the flatness of the sub-frame and the body mounting surface, the Z-direction height difference and the lap joint clearance, all within the tolerance range; the test bolt performance grade, material core hardness, gasket hardness, and load-holding capacity all meet the design requirements. According to the frictional anti-loose mechanism of the threaded connection, the relatively large frictional connection, as the working time is lengthened, the residual pre-tightening force accounts for a relatively high percentage of the pre-tightening force. Finally, the bolt friction factor is adjusted from 0.1 to 0. 16 to 0. 2 to 0. 45. Compared with the trial verification, the detected torque values ​​after the line is as shown in Table 2, and the torque is within the design range.
Comparing the test data of Table 1 and Table 2, after the friction factor is increased, the torque attenuation failure is effectively improved. The smaller the friction factor, the larger the axial force of the bolt provided after pre-tightening, but it is not conducive to the maintenance of the torque, and the torque is easily attenuated. On the contrary, the larger the friction factor, although it does not provide a large tightening axial force, but it is more conducive to the maintenance of the torque, the torque is not easily attenuated. Therefore, in the later design, the use of threaded fasteners should be comprehensively considered, and the determination of the friction factor should be adjusted according to the material and structure of the actual connecting parts.
  2.3 Plastic deformation of the connected parts
After the endurance test of a vehicle, the suspension control arm and the sub-frame coupling bolts generate torque attenuation. The disassembly control arm finds a slight indentation on the aluminum alloy base that is in contact with the end face of the assembly bolt hex flange, as shown in Figure 4. Check that the thread structure is normal and the bolts are not elongated.

Failure mechanism. The mounting base is made of aluminum alloy, grade 6082-T6, material yield strength is 260 MPa, and tensile strength is 310 MPa. Indentation at the assembly location indicates that the material has undergone plastic deformation, that is, the stress at the installation location exceeds the yield strength of the material. The failure position is attached to the strain gauge, and the maximum stress of the indentation position measured by the actual road test is 290 MPa, which is much larger than the yield strength of the material. During the endurance test of the whole vehicle, the installation position is constantly subjected to alternating load. When the stress exceeds the yield strength of the material, the base is plastically deformed, and the axial force of the joint position is tightly reduced, and finally the torque is attenuated.
Corrective measures. For this failure, the initial countermeasures are two solutions: (1) Change the mounting base to a material with higher yield strength; (2) Increase the bearing area of ​​the mounting position, that is, add a gasket between the mounting surfaces or directly increase the mounting bolts. Flange area. Considering the comprehensive cost and rectification cycle, it is easier to achieve the addition of gaskets between the mounting surfaces (see Figure 5) and the cost is low.
The original bearing area is S 0 , the inner surface of the bolt flange contact is 14. 5 mm, and the outer diameter is 28. 6 mm.
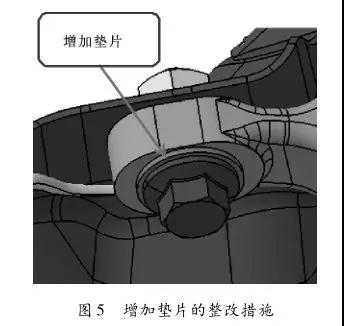
As shown in Figure 5, the gasket has an inner diameter of 14.5 mm and an outer diameter of 32 mm. The thickness of the gasket is 2 mm, and the pressure-bearing area after the gasket is increased:
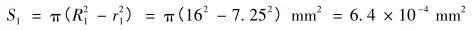
After the gasket is added, the maximum stress at the failure position of the bad road test is reduced to 236 MPa, which is less than the yield strength of the material, and the plastic deformation of the base is avoided, thereby eliminating the torque attenuation.
3. Conclusion
With the development of the industry, the use of threaded fasteners has become more widespread. In order to ensure the reliability of the threaded fastening connection, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the process guarantee capability, material characteristics, friction factor, structural form and working environment of the connected parts, and the selection of the torque is also subject to strict check calculation. In the product design phase, the more factors are considered, the less failures are generated later.
Author: heavy Rui, Zhang Hong, Fan Qiuzhen
Source: Great Wall Motor Co., Ltd. Technology Center
Hebei Automobile Engineering Technology Research Center
There is long history in China to use natural herb and flavor.Benifit by abundant forest and plant resources in China,we take a lot of natural plant extracts to benefit people`s daily life.These products includes forest essential oil,grass essential oil,fruit essential oils,natural Borneol ,Myricetin etc.It can be usded in many indutreis such as pharmaceutical
and medicine,cosmetic,perfumery,chemical industry,food industry etc.More and more people prefer to choose natural products. We supply following products in this segment:
Flavour And Fragrance
Anise Oil
Peppermint oil
Menthol
Raspberry ketone
Linalool
Benzaldehyde
Benzyl benzoate
Hydroquinone
Dihydromyrcenol
Natural Garlic Oil
Natural Perilla Oil
Natural Spearmint Oil
Natural Cinnamon oil
Natural Wintergreen Oil
Natural Linalool
Natural Ho oil
Natural Camphor powder
Citral

Flavour And Fragrance
Natural Linalool Oil,Pure Natural Garlic Oil,Menthol Oil,Natural Wintergreen Oil
shijiazhuang yihe-chem co.,ltd , https://www.yihe-chem.com