The gauge is one of the standard instruments for measuring the verticality. The conventional gauge calibration method mainly uses a special gauge (see Figure 1) or a photoelectric autocollimator to calibrate the angular deviation of the four corners of the gauge by the self-closing principle. . For large-scale gauge calibration (above 500mm), due to its large size and heavy weight, the positioning of the other gauge and the adjustment of the photoelectric autocollimator are inconvenient, and the use of a coordinate measuring machine can easily solve this problem. There are two methods for detecting the gauge on the coordinate measuring machine. One is to directly construct the coordinate system on the square gauge, and the measured value of the four corners is directly obtained in one measurement. The method is simple and convenient, but the detection result includes the coordinate measuring machine. Its own verticality and straightness error. Therefore, this method is only suitable for the detection of low-precision square gauges. For high-precision square gauges, the second flip multi-position method is adopted, that is, the position measurement can be effectively separated by position placement in different directions. The influence of the verticality and straightness of the machine itself can be quickly measured by the coordinate machine's edit measurement program, and then the closed principle is used for data processing, which can improve the uncertainty of each angle measurement.
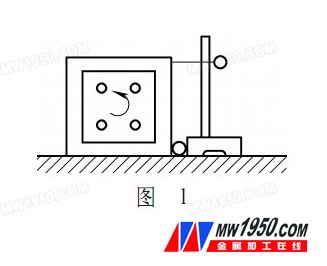
Detection method
(1) Coordinate measuring machine conventional measurement method
The square gauge is placed directly on the coordinate measuring machine, and the coordinate system is established on the square gauge. The angle of the four angles is directly obtained in one measurement. The method is simple and convenient, but the detection result contains the verticality and straightness error of the coordinate measuring machine itself. The uncertainty of the measurement is completely dependent on the uncertainty of the angle measured by the CMM. If you want to separate the influence of the CMM on the measurement, you can use a high standard standard deviation of the known angular deviation for comparative measurement.
(2) Coordinate measuring machine flip measurement method
The inversion measurement method separates the influence of the measurement error caused by the verticality and the straightness of the measuring machine through the placement measurement of the different positions of the measured elements and the subsequent data processing. It does not require the comparison of the standard, and directly improves the measurement. The uncertainty of the measured measurement of the measured element by the measuring machine.

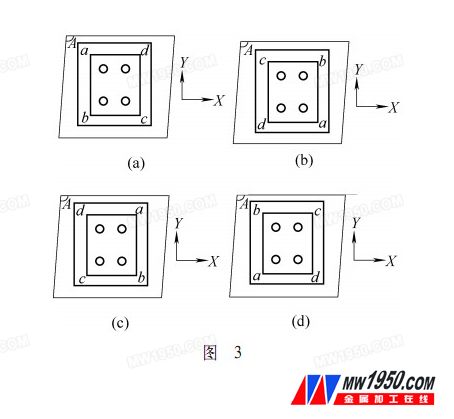
figure 2
The measurement process is as follows. The square gauge is placed on the coordinate measuring machine table, as shown in Fig. 2, and the square gauge is divided into four positions for detection according to Fig. 3, wherein Fig. 3b is rotated in the original position by Fig. 3a. °, FIG. 3c is FIG. 3a flipped by 180° in the original position, and FIG. 3d is rotated by 180° in the original position in FIG. 3c, and the overlap of the front and rear positions should be ensured after the turning. The coordinate system is established at each position and the four angles of the gauge are measured.
2. Data processing
Suppose the angle A is the measurement angle deviation caused by the angle of the X and Y axes and the straightness in the XY working plane of the measuring machine. Let Δa, Δb, Δc, Δd be the actual angular deviation of the square gauge, ai, bi, ci, di For the measurement results of the coordinate measuring machine, the measured relationship of the angles of the four positions is as follows: a1=90°-A+Δa, b 1=90°-A+Δb, c 1=90°-A+Δc,d 1 = 90 ° - A + Δd.
Position b: a2 = 90 ° - A + Δa, b2 = 90 ° - A + Δb, c2 = 90 ° - A + Δc, d2 = 90 ° - A + Δd.
Position c: a3 = 90 ° - A + Δa, b3 = 90 ° - A + Δb, c3 = 90 ° - A + Δc, d3 = 90 ° - A + Δd.
Position d: a4 = 90 ° - A + Δa, b4 = 90 ° - A + Δb, c4 = 90 ° - A + Δc, d4 = 90 ° - A + Δd.
Adding the angular relationships of the four positions to obtain the following relationship
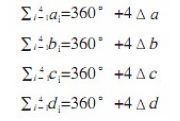
Then there is the actual deviation of the four corners of the square
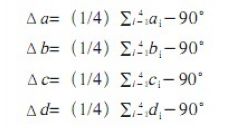
It can be seen from the above calculation that the results of the four corners are used in the measurement process by the reverse and self-closing principle, the error separation of the measuring equipment and the average processing of the measurement results, effectively improving the reliability of the measurement results, and separating The influence of the uncertainty brought about by the geometric accuracy error of the measuring machine is revealed.
3. Conclusion
Through mathematical derivation, this paper focuses on the use of symmetric reverse elimination method and self-closing principle to deal with the results of four angles, which not only improves the accuracy of measurement, but also can detect larger scales in different precision measuring machines. Explore the feasible theoretical basis.
Aluminum Camlock Fitting Type D Coupler,Aluminum Part D Camlock, Aluminum Type D Cam and Groove Fitting
Cixi Chengtuo Hardware Parts Factory , https://www.ibccoupling.com