Abstract Several mature rapid prototyping methods are briefly introduced. The application of rapid prototyping technology in the field of ceramics is introduced, and the problems and development directions of the technology for producing ceramic parts are discussed.
Key words rapid prototyping; ceramic
CLC number TQ174.6 + 2 Document code A
Article ID 1001-4381 (1999) 11-0037-04
Applications of Rapid Prototyping Technique in the Field of Ceramics
Abstract: Some rapid protoptyping mathods were introduced brief with emphasis on applications of rapid prototyping technique in the field of ceramics. The problems and prospect of ceramics preparation with the techniques were also discussed.
Key words : rapid prototyping;ceramics
Rapid Prototyping and Manufacturing (RP or RP&M) or Solid Free Form Fabrication (SFF) is a new technology developed in the mid-1980s that changed the traditional “removal†processing method to “ Increase the "processing method. RP technology combines computer-aided design, laser, photochemistry and polymer technology, and its application field is expanding with the combination of RP technology and other material processing technologies. The basic principle of RP technology is to first obtain a series of cross-sections according to the product design drawing or “reverse methodâ€. The CNC laser beam processes and superimposes the material layer by layer according to the outline of each layer or the inner grid line until the whole system is completed. Pieces. RP technology eliminates the need for machining or any molds to create complex-shaped parts directly from CAD models, resulting in shorter product development cycles, increased productivity, and lower production costs.
In 1987, 3D Systems of the United States exhibited the first commercial RP system SLA-1. After that, RP technology developed rapidly and was applied in many departments. Its main uses include rapid prototyping technology production model for product design verification, evaluation, performance testing, etc., production of injection molds, functional materials, combined with traditional manufacturing processes to manufacture molds and metal parts.
1 RP technology type [1~4]
At present, more mature rapid prototyping methods include SLA, LOM, SLS, FDM, and 3DP.
The Stereo-Lithography Apparatus (SLA) is the earliest practical product of RP technology. The SLA process is shown in Figure 1. The process is to first design a three-dimensional solid model through CAD, convert the model into a standard format STL file, use a discrete program to slice the model, design the scan path, and the generated data will accurately control the motion of the scanner and the lift table. The laser beam generated by the laser is focused and irradiated onto the surface of the liquid photosensitive resin of the container, so that a layer of resin in a specific area of ​​the surface is solidified, and the lifting platform is lowered by a certain distance, so that the SLA device produces the workpiece layer by layer.
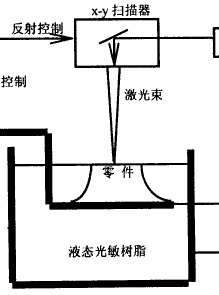
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the SLA process
Fig.1 Schematic representation of SLA process
The common raw material for SLA technology is thermosetting photosensitive resin, which is mainly used to manufacture a variety of molds, models, etc., and can also replace the wax mold in investment precision casting by adding other components with SLA prototype mold. SLA technology has a faster forming speed and higher precision, but it will inevitably generate stress or cause deformation due to shrinkage during curing of the resin. The development of photosensitive materials with small shrinkage, fast curing and high strength is the development trend.
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) is a method of forming a film material layer by layer into a desired shape and then superimposing it together. The LOM process differs from the SLA process in that the photocured scanning motion in the SLA is changed to the laser cutting motion in the LOM.
The commonly used materials for LOM technology are paper, metal foil, plastic film, ceramic film, etc. In addition to molds and models, structural or functional parts can be directly fabricated. LOM technology has a high forming speed and low manufacturing cost, but due to the limited thickness of the material film, the untreated surface is not smooth and needs to be reprocessed.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is to spread the powder material into a thin layer with a certain thickness. The laser scans the powder in a certain area and then grinds it on the sintered layer. Solid parts. The key to its technology is to adjust the laser beam for powder sintering.
Next page
Other Ornaments/Ceiling/Moulding
Other Ornaments,Other Ceiling,Other Moulding
Cornice And Moldng,Other Ceiling Co., Ltd. , http://www.nsceiling.com